The Power of Love
A Comprehensive Exploration of Humanity's Most Profound Emotion
Introduction to Love
Love is one of the most complex and profound human emotions, influencing our behavior, decisions, and overall well-being. Throughout history, love has been the subject of philosophical debates, scientific studies, and artistic expressions across all cultures.
From a biological perspective, love involves complex neurochemical processes, while psychologists view it as a combination of emotions, behaviors, and beliefs. Sociologists examine how love functions within societies and relationships.
The Psychology of Love
Psychologists have identified several components that make up the experience of love:
- Intimacy: Feelings of closeness, connectedness, and bondedness
- Passion: Physical attraction and sexual consummation
- Commitment: The decision to remain with another and work to maintain the relationship
Sternberg's Triangular Theory of Love
Psychologist Robert Sternberg proposed that love consists of three components that can be combined to form different types of love:
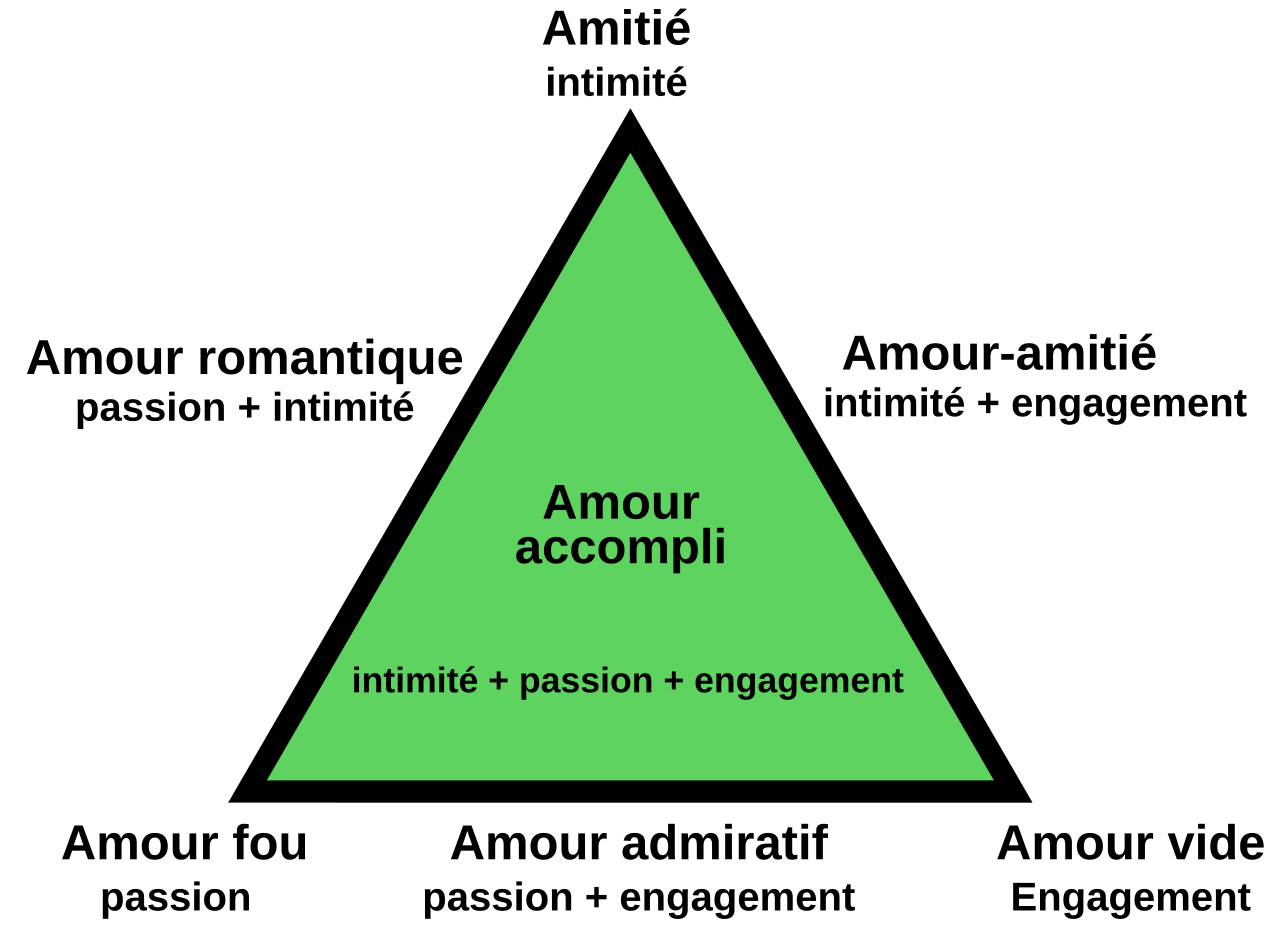
The combination of these components creates seven different kinds of love experiences (nonlove, liking, infatuated love, empty love, romantic love, companionate love, fatuous love, and consummate love).
Types of Love
Love manifests in many forms throughout our lives and relationships. Here are the most significant types:
Romantic Love
Characterized by intimacy and passion, romantic love involves physical attraction and emotional connection without immediate commitment.
Platonic Love
A deep, non-romantic connection between friends that involves intimacy without sexual attraction.
Familial Love
The bond between family members, characterized by strong commitment and intimacy, often without romantic passion.
Self-Love
A fundamental form of love involving acceptance, care, and respect for oneself, crucial for mental health.
Unconditional Love
Love without limitations or conditions, often seen in parent-child relationships or long-term partnerships.
Compassionate Love
Characterized by mutual respect, attachment, affection, and trust, typically found in long-term relationships.
The Biology of Love
Love isn't just an emotion—it's a complex biological process involving multiple systems in the body:
Neurochemistry of Love
- Dopamine: Creates feelings of euphoria and pleasure (reward system)
- Oxytocin: "The love hormone" that promotes bonding and attachment
- Serotonin: Affects mood and obsessive thinking in early romantic love
- Norepinephrine: Causes the racing heart and excitement of new love
Evolutionary Perspectives
From an evolutionary standpoint, love developed as a survival mechanism to promote:
- Pair bonding for child-rearing
- Social cohesion within groups
- Long-term cooperation between individuals
Cultural Aspects of Love
Cultural influences shape how we experience and express love:
Western vs. Eastern Concepts
Western cultures often emphasize romantic love as the basis for marriage, while many Eastern cultures have traditionally viewed love as something that develops after marriage.
Love in Different Historical Periods
The concept of romantic love has evolved significantly throughout history, from the courtly love of medieval times to today's more individualistic notions.
Love Languages
Gary Chapman's theory suggests people express and receive love in five primary ways: words of affirmation, quality time, receiving gifts, acts of service, and physical touch.
The Importance of Love in Human Life
Love plays crucial roles in our psychological and physical well-being:
- Mental Health: Loving relationships reduce stress, anxiety, and depression
- Physical Health: People in loving relationships tend to have stronger immune systems and live longer
- Personal Growth: Love challenges us to grow, compromise, and develop empathy
- Social Connection: Love forms the foundation of families and communities
Conclusion
Love is a multifaceted experience that transcends simple definition. It exists at the intersection of biology, psychology, and culture, shaping human experience in profound ways. Whether romantic, platonic, or self-directed, love remains one of the most powerful forces in human life, driving connection, creativity, and meaning.
Understanding the different aspects of love can help us cultivate healthier relationships and a more compassionate world. As research continues to uncover the mysteries of love, one truth remains constant: love in all its forms is essential to the human experience.